Using Heatmaps for UX sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
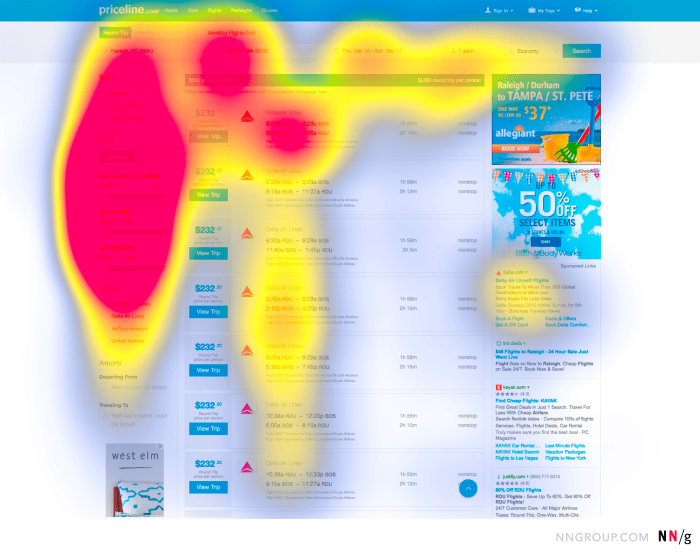
Heatmaps are a powerful tool in UX design, providing valuable insights into user behavior on websites and applications. From click heatmaps to scroll heatmaps, each type offers unique perspectives that can revolutionize how we understand and optimize user experiences.
Introduction to Heatmaps for UX

Heatmaps are visual tools used in UX design to analyze user behavior on websites or applications. They provide insights into how users interact with a site by showing areas of high and low activity.
Types of Heatmaps
- Click Heatmaps: Show where users click the most on a page, indicating areas of interest.
- Scroll Heatmaps: Display how far down a page users scroll before leaving, helping to optimize content placement.
- Move Heatmaps: Track mouse movement to understand user engagement and interest in specific elements.
- Attention Heatmaps: Highlight elements that receive the most visual attention from users.
Importance of Heatmaps in UX
Heatmaps play a crucial role in UX analysis as they help designers and developers make informed decisions based on user behavior data. By understanding how users interact with a website or application, improvements can be made to enhance the overall user experience and increase conversion rates.
Benefits of Using Heatmaps
Heatmaps are powerful tools that provide valuable insights into user interactions with a website, helping businesses optimize their design and layout for a better user experience. By visually representing user behavior, heatmaps offer several benefits:
Identifying Hotspots and Cold Zones
- Heatmaps can show which areas of a webpage receive the most attention from users, indicated by “hotspots” of high interaction. This information helps designers prioritize important content and calls-to-action.
- Conversely, “cold zones” with low interaction can pinpoint areas that may need improvement or redesign to attract more user engagement.
Scroll Depth Analysis
- Heatmaps can track how far users scroll down a webpage, revealing where most users lose interest or abandon the page. This data can inform content placement and help optimize the layout to keep users engaged throughout the page.
Click Tracking and User Behavior
- By recording where users click on a webpage, heatmaps provide insights into user behavior and preferences. Designers can analyze this data to optimize the placement of buttons, links, and other interactive elements for a more intuitive user experience.
Mobile Responsiveness
- Heatmaps can differentiate between desktop and mobile user interactions, helping designers create responsive designs that cater to the unique browsing behaviors of each device. This ensures a seamless user experience across all platforms.
Types of Heatmaps: Using Heatmaps For UX
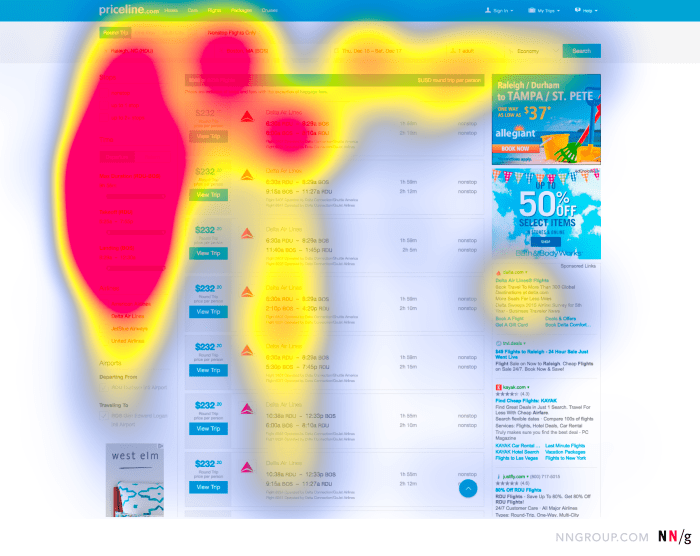
Heatmaps come in various types, each offering unique insights into user behavior on a website. Let’s explore the different types of heatmaps and their relevance in UX research.
Click Heatmaps
Click heatmaps track where users are clicking on a webpage. By visualizing the most clicked areas, designers can understand which elements are attracting the most attention. This type of heatmap helps in optimizing the placement of important buttons, links, or CTAs for better user engagement.
Scroll Heatmaps
Scroll heatmaps indicate how far down the page users are scrolling. They show where users are spending the most time and where they tend to abandon the page. This information helps in identifying the optimal length of a webpage and determining which content is most engaging for users.
Move Heatmaps
Move heatmaps track the movement of the cursor on a webpage. They reveal patterns of user attention and behavior, such as areas where users hover or hesitate. Designers can use this data to enhance user experience by placing important information where users naturally tend to focus.
Implementing Heatmaps for UX Analysis
When it comes to setting up heatmaps on a website or application, there are several steps involved in the process. It’s important to follow these steps carefully to ensure accurate data collection and analysis for improving the user experience.
Setting Up Heatmaps
- Choose a reliable heatmap tool that meets your specific needs and budget.
- Install the heatmap tracking code on all relevant pages of your website or application.
- Customize the heatmap settings to track specific user interactions and behaviors.
- Allow the heatmap tool to collect data over a period of time to gather meaningful insights.
Interpreting Heatmap Data, Using Heatmaps for UX
- Focus on areas of high user engagement, such as where users are clicking the most.
- Identify areas of low engagement to pinpoint potential issues or areas for improvement.
- Look for patterns and trends in user behavior to inform UX design decisions.
- Consider combining heatmap data with other analytics tools for a more comprehensive analysis.
Incorporating Heatmap Analysis into UX Design
- Use heatmap data to inform website or application redesigns for a more user-friendly experience.
- Test different design elements based on heatmap insights to optimize user interactions.
- Regularly monitor heatmap data to track the impact of design changes on user behavior.
- Collaborate with UX designers and developers to implement heatmap findings effectively.